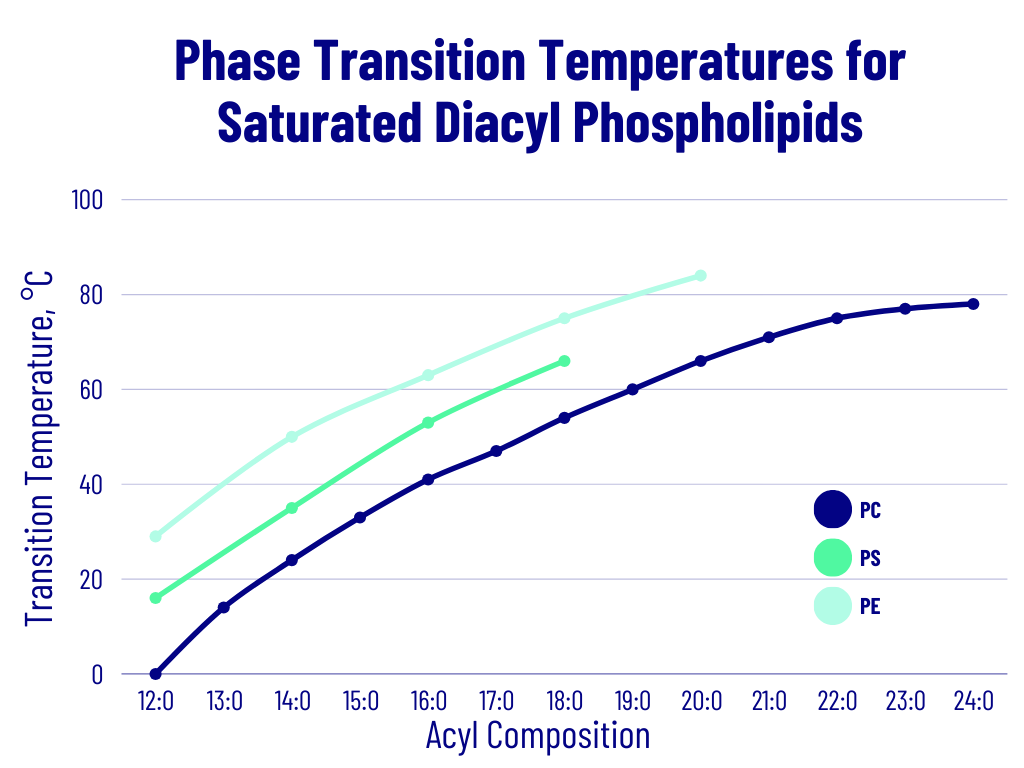
| Phosphatidylcholine | Phosphatidylglycerol (Sodium Salt) | |||
| Product | Tm (°C) | Product | Tm (°C) | |
| 12:0 PC (DLPC) | -2 | 12:0 PG (DLPG) | -3 | |
| 13:0 PC | 14 | 14:0 PG (DMPG) | 23 | |
| 14:0 PC (DMPC) | 24 | 16:0 PG (DPPG) | 41 | |
| 15:0 PC | 35 | 18:0 PG (DSPG) | 55 | |
| 16:0 PC (DPPC) | 41 | 18:1 PG (DOPG) | -18 | |
| 17:0 PC | 50 | 16:0-18:1 PG (POPG) | -2 | |
| 18:0 PC (DSPC) | 55 | Phosphatidylserine (Sodium Salt) | ||
| 19:0 PC | 62 | 14:0 PS (DMPS) | 35 | |
| 20:0 PC | 66 | 16:0 PS (DPPS) | 54 | |
| 21:0 PC | 71 | 18:0 PS (DSPS) | 68 | |
| 22:0 PC | 75 | 18:1 PS (DOPS) | -11 | |
| 23:0 PC | 79.5 | 16:0-18:1 PS (POPS) | 14 | |
| 24:0 PC | 80.3 | Phosphatidic Acid (Sodium Salt) | ||
| 16:1 PC | -36 | 12:0 PA (DLPA) | 31 | |
| 18:1c9 PC (DOPC) | -17 | 14:0 PA (DMPA) | 52 | |
| 18:1t9 PC | 12 | 16:0 PA (DPPA) | 65 | |
| 18:1c6 PC | 1 | 18:0 PA (DSPA) | 75 | |
| 22:1c13 PC | 13 | 18:1 PA (DOPA) | -4 | |
| 18:2 PC | -57 | 16:0-18:1 PA (POPA) | 28 | |
| 18:3 PC | -60 | Cardiolipin | ||
| 14:0 CL | 47 | |||
| 16:0 CL | 62.2 | |||
| 20:4 PC | -69 | Phosphatidylethanolamine | ||
| 14:0-16:0 PC | 35 | Tm (°C) | Th (°C) | |
| 14:0-18:0 PC | 40 | 12:0 PE (DLPE) | 29 | |
| 16:0-14:0 PC | 27 | 14:0 PE (DMPE) | 50 | |
| 16:0-18:0 PC | 49 | 16:0 PE (DPPE) | 63 | 118 |
| 16:0-18:1 PC (POPC) | -2 | 18:0 PE(DSPE) | 74 | 100 |
| 16:0-22:6 PC | -27 | 20:0 PE | 83 | 96 |
| 18:0-14:0 PC | 30 | 18:1c9 PE (DOPE) | -16 | 10 |
| 18:0-16:0 PC | 44 | 18:1t9 PE | 38 | 64 |
| 18:0-18:1 PC | 6 | 18:2 PE | -40 | -15 |
| 18:1-16:0 PC | -9 | 18:3 PE | -30 | |
| 18:1-18:0 PC | 9 | 16:0-18:1 PE (POPE) | 25 | 71 |
Formulating with lipids has many nuances, with perhaps temperature considerations being the most important processing aid. Individually, phase transition temperatures are provided as Tm and Th. Let’s discuss what these terms meanings and how these characteristics impact processing, as well as how you may want to delve into temperature changes during formulation troubleshooting.
Click here for our blog, Navigating Tm and Th for Optimal Processing and Troubleshooting Success!
References
Thermotropic Phase Transitions of Pure Lipids in Model Membranes and Their Modifications by Membrane Proteins, Dr. John R. Silvius, Lipid-Protein Interactions, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1982. Reprinted with permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Lipid Thermotropic Phase Transition Database (LIPIDAT) – NIST Standard Reference Database 34
